Introduction to Lyme Disease Teeth
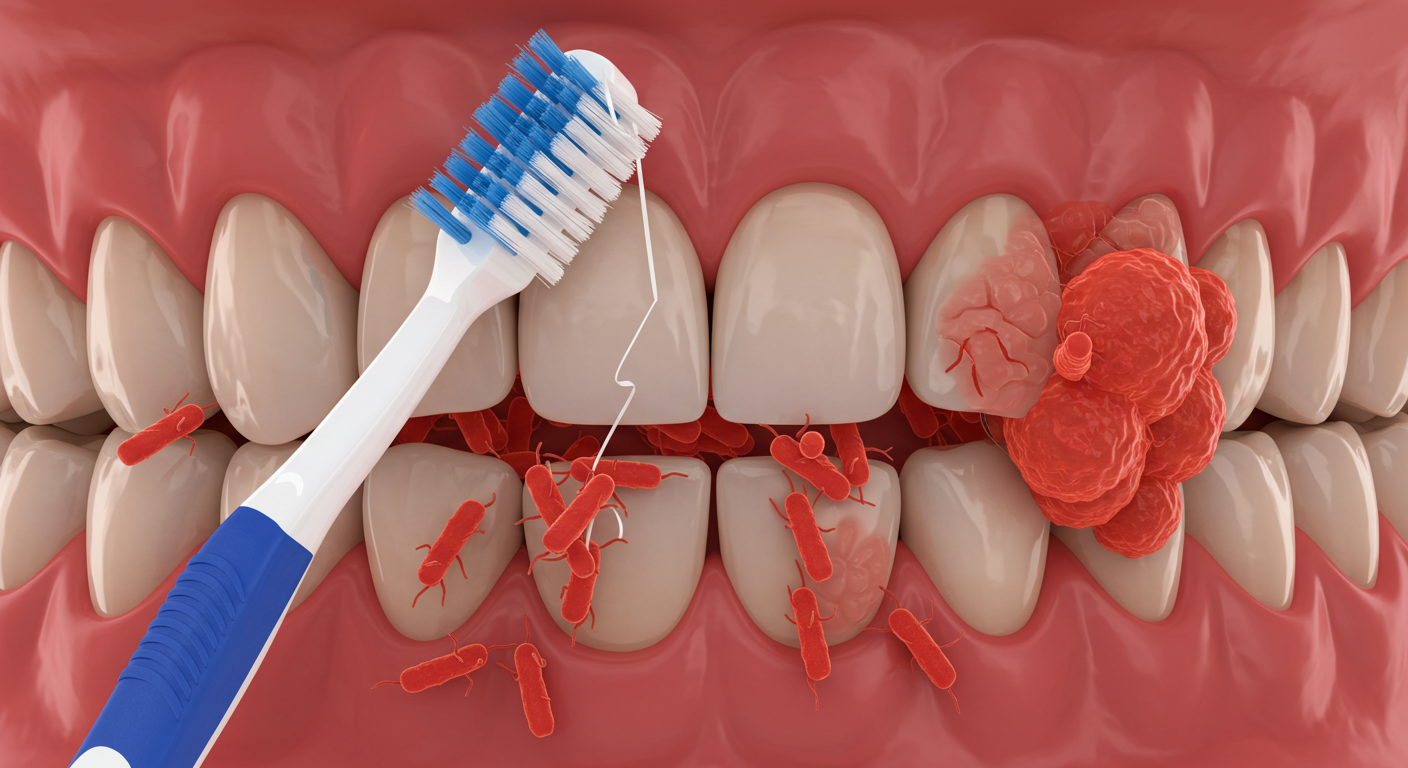
Lyme disease teeth doesn’t just affect the body—it can also have a serious impact on dental health. The spirochetes, bacteria responsible for Lyme disease, can thrive in the mouth, leading to gum inflammation, chronic periodontitis, and potential tooth damage. An acidic oral environment (low pH) creates the perfect conditions for these harmful bacteria to multiply, weakening the gums and the tissues that support the teeth.
Surprisingly, research suggests that Lyme bacteria can hide inside root canal-treated teeth, posing additional risks to oral health. This highlights the importance of testing these teeth for spirochetes and other harmful bacteria to prevent further complications.
One major concern is chronic periodontitis, a severe gum infection linked to Lyme disease, which can cause:
- Swollen, bleeding gums
- Persistent bad breath
- Loose or shifting teeth
Unfortunately, Lyme disease-related dental problems are often overlooked, yet they can worsen if not addressed early. Regular dental check-ups, proper oral hygiene, and early intervention are essential to managing these risks. By staying informed and proactive, individuals with Lyme disease can protect their teeth, gums, and overall well-being from its long-term effects.
Lyme Disease and Its Impact on Health: Understanding the Three Stages
Lyme disease progresses through three main stages: early localized, early disseminated, and late disseminated. Each phase presents unique symptoms that can affect overall health, including dental health, which is often overlooked.
Stage 1: Early Localized Lyme Disease
In the early localized phase, the most noticeable sign is a red, expanding rash known as erythema migrans. This stage may also bring flu-like symptoms, including:
- Fever
- Chills
- Fatigue
- Headaches
- Muscle or joint pain
Stage 2: Early Disseminated Lyme Disease
If left untreated, Lyme disease can advance to the early disseminated phase within weeks or months. Symptoms at this stage may worsen and include:
- Multiple skin rashes
- Facial paralysis (Bell’s palsy)
- Meningitis
- Irregular heartbeats
Stage 3: Late Disseminated Lyme Disease
In the late disseminated phase, serious health complications can develop, such as:
- Chronic arthritis
- Nerve problems
- Cognitive difficulties
Lyme Disease and Its Impact on Oral Health
Recent studies suggest that Lyme disease bacteria (spirochetes) can also affect dental health. This can lead to:
- Gum inflammation
- Increased risk of oral infections
- Lyme disease teeth issues, impacting overall oral hygiene
The Importance of Early Detection and Treatment
Early detection and antibiotic treatment are crucial to prevent Lyme disease from spreading and causing long-term complications. Taking proactive steps such as:
- Seeking medical treatment in the early stages
- Maintaining good oral hygiene
- Scheduling regular dental check-ups
Can Lyme disease cause dental problems or tooth issues?
Lyme disease, caused by the bacteria Borrelia burgdorferi, can lead to several dental and oral health issues, including temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJ) and facial pain. The bacteria can damage the muscles and ligaments in the jaw, triggering TMJ disorder. This condition often causes jaw pain, trouble moving the jaw, and even misaligned teeth. Additionally, Lyme disease can inflame facial nerves, leading to persistent facial pain and discomfort.
Some common oral health symptoms linked to Lyme disease include jaw pain, trouble chewing or swallowing, facial numbness, sensitive teeth, and in severe cases, tooth loss. The impact on Lyme disease teeth and overall oral health can be significant, often causing chronic pain and making everyday activities like eating and speaking difficult. This can greatly reduce a person’s quality of life if not addressed properly.
Recent research highlights that Lyme disease bacteria can also affect the gums and teeth, potentially worsening conditions like gum disease or tooth decay. This makes it even more important for individuals with Lyme disease to pay close attention to their oral health. Regular dental check-ups and proper oral hygiene can help manage these issues effectively.
Proper treatment and management of Lyme disease are crucial to minimize its effects on oral health. Early intervention can prevent complications like TMJ disorder and protect Lyme disease teeth from long-term damage. If you have Lyme disease, it’s essential to work with both your healthcare provider and dentist to address any oral health concerns and maintain overall well-being.
By staying informed and proactive, individuals can better manage the connection between Lyme disease and dental health, ensuring a healthier smile and improved quality of life. This updated information emphasizes the importance of understanding how Lyme disease impacts oral health and taking steps to prevent complications.
How Lyme Disease Affects Dental Health: Key Concerns
Lyme disease, caused by the Borrelia bacteria, can significantly impact dental health, particularly during procedures like tooth extractions and in the development of gum problems. During a tooth extraction, there’s a risk that the bacteria responsible for Lyme disease could be exposed. This exposure might worsen symptoms or spread the infection, making it crucial for individuals with Lyme disease to inform their dentist about their condition before any dental work.
Connection Between Lyme Disease and Jaw Issues
Lyme disease is also linked to temporomandibular joint dysfunction (TMJ), a condition that causes pain and discomfort in the jaw. This can make everyday activities like chewing or speaking difficult. For those with Lyme disease teeth and jaw concerns, managing TMJ symptoms becomes an important part of their overall care.
Gum Health and Lyme Disease
Another area of concern is gum health. Lyme disease can lead to gum inflammation and periodontal disease, which, if untreated, may cause gum recession, tooth sensitivity, and even tooth loss. Recent studies suggest that the bacteria causing Lyme disease can also weaken the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off gum infections. This highlights the importance of maintaining good oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups for those with Lyme disease.
Why Early Action Matters
Individuals with Lyme disease should be aware of these potential dental issues and work closely with their healthcare and dental providers to address them. Early detection and treatment of gum problems or jaw disorders can prevent long-term damage to Lyme disease teeth and improve overall quality of life.
By staying informed and proactive, patients can better manage the connection between Lyme disease and dental health, ensuring a healthier smile and fewer complications. This updated information emphasizes the importance of understanding how Lyme disease impacts oral health and taking steps to protect your teeth and gums.
How Lyme Disease Affects Oral Health: What You Need to Know
Lyme disease, caused by the Borrelia bacteria, can trigger surprising oral health problems that many people overlook. Beyond its well-known symptoms, it may lead to issues like dry mouth, tooth pulp inflammation (pulpitis), and burning mouth syndrome. These problems often tie back to nerve damage caused by the bacteria, which can disrupt the central nervous system and harm nerves in the mouth.
Dry Mouth and Taste Changes
One common symptom is dry mouth, which happens when Lyme disease interferes with saliva production. Without enough saliva, the mouth becomes a breeding ground for bacteria, raising the risk of cavities and gum disease. Some people also notice changes in taste or find it harder to swallow—another sign of nerve-related issues linked to Lyme.
Tooth Sensitivity and Pain
Lyme disease can cause inflammation in the tooth’s inner pulp (pulpitis), leading to sharp sensitivity or throbbing pain. This is especially concerning for those with Lyme disease teeth issues, as untreated inflammation may spread or worsen. Recent studies suggest that Lyme bacteria might even hide in damaged teeth, making regular dental check-ups critical for early detection.
Burning Mouth Syndrome
A burning or tingling sensation in the mouth, tongue, or lips—known as burning mouth syndrome—is another red flag. This discomfort can feel like a mild sunburn and is often linked to nerve irritation caused by Lyme disease.
Why Dental Care Matters for Lyme Patients
Ignoring these oral symptoms can lower quality of life, making eating, speaking, or even smiling painful. For example, chronic dry mouth might speed up tooth decay, while untreated pulpitis could lead to infections. New research (2023) also shows that Lyme-related nerve damage might weaken the immune system’s ability to fight oral infections, creating a cycle of problems.
The key takeaway? If you have Lyme disease, prioritize your dental health. Tell your dentist about your diagnosis, especially if you notice unusual symptoms like dry mouth, taste changes, or tooth pain. Early care can prevent minor issues from turning into major Lyme disease teeth complications.
By staying informed and proactive, you can protect your smile and overall well-being. Simple steps like staying hydrated, using saliva-boosting products, and scheduling regular cleanings make a big difference. Don’t let Lyme disease silently harm your oral health—take action today!
This guide highlights the latest findings on Lyme disease and dental health, offering clear, actionable tips to keep your mouth healthy.
Oral Symptoms of Lyme Disease: Why They’re Often Confused with Dental Problems
Lyme disease doesn’t just affect joints or energy levels—it can also create oral symptoms that look like common dental issues. Dry mouth, tooth sensitivity, inflamed tooth pulp (pulpitis), jaw muscle pain, and TMJ discomfort are all signs that might trick dentists into thinking it’s a routine problem. For example, someone with Lyme disease teeth issues might complain about sharp pain when eating ice cream, which could easily be mistaken for a cavity or cracked tooth.
The Danger of Misdiagnosis
Why does this mix-up matter? If these symptoms are written off as “just a dental problem,” the real cause—Lyme disease—might go untreated. Delayed diagnosis allows the infection to spread, increasing the risk of severe complications like chronic pain or nerve damage. Recent studies (2023) show that Lyme bacteria can hide in oral tissues, directly irritating nerves and triggering inflammation. This means even a simple toothache could be a clue to a bigger health issue.
How Lyme Bacteria Harm Oral Health
The Borrelia bacteria behind Lyme disease don’t just stay in the bloodstream. They can settle in the mouth, causing problems like gum inflammation or persistent dry mouth (which raises cavity risk). For those with Lyme disease teeth concerns, the body’s weakened immune response might also make it harder to fight off infections, worsening issues like pulpitis or TMJ flare-ups.
What Dentists Need to Know
Dental providers play a key role in spotting Lyme-related symptoms. If a patient’s “tooth pain” doesn’t improve with fillings or root canals, or if their gums stay inflamed despite good hygiene, Lyme disease could be the hidden culprit. Simple blood tests or referrals to a Lyme specialist can help crack the case.
Don’t Ignore These Red Flags
- Unexplained dry mouth that won’t go away
- Tooth sensitivity without visible decay
- Jaw pain that spreads to the face or neck
- Tingling or burning sensations in the mouth
Early action can stop Lyme disease from damaging both oral health and overall well-being. Patients should tell their dentist if they’ve had tick bites or live in high-risk areas—details that connect the dots.
Bottom Line
Lyme disease and dental health are more linked than most people realize. By staying alert to unusual symptoms and asking the right questions, dentists can help patients get faster treatment and avoid long-term harm. For anyone with Lyme disease teeth or mouth issues, teamwork between dental and medical providers is the best way to protect their smile—and their health.
Why Choose Wellness Dental for Lyme Disease and Oral Health?
At Wellness Dental, we’re passionate about whole-body dental care, combining advanced treatments like ozone therapy and gentle, minimally invasive techniques. If you’re worried about how Lyme disease might be affecting your teeth, gums, or overall oral health, we’re here to help. Our team specializes in identifying and addressing the hidden links between Lyme disease and dental wellness, ensuring your care goes beyond “just fixing teeth.”
How We Connect Oral Health and Lyme Disease
During your visit, we’ll explore how your oral health ties into your overall wellness—especially if Lyme disease is part of your story. Did you know Lyme bacteria can hide in the mouth, causing issues like jaw pain, gum inflammation, or even Lyme disease teeth sensitivity? We use cutting-edge tools and holistic strategies to spot these problems early, stopping them from worsening your health.
Holistic Care That Works With Your Body
We don’t just treat symptoms—we dig deeper. For example, ozone therapy isn’t just about killing harmful bacteria; it also boosts healing in gums and teeth damaged by Lyme-related inflammation. Recent studies (2024) show that Lyme bacteria in the mouth can weaken the immune system, making personalized, integrative care even more critical.
Your Personalized Plan
Whether you’re dealing with chronic dry mouth, unexplained tooth pain, or jaw stiffness linked to Lyme disease, we create a tailored plan just for you. Our goal? To protect your Lyme disease teeth and gums while supporting your body’s natural healing process. We’ll also collaborate with your healthcare providers to ensure every part of your health gets the attention it deserves.
Take Control of Your Health Today
Don’t let Lyme disease silently harm your smile. By choosing Wellness Dental, you’re opting for care that understands the big picture. Our proactive approach helps you:
- Reduce oral inflammation linked to Lyme
- Strengthen gums and teeth against bacterial damage
- Prevent long-term issues like tooth loss or TMJ disorders
Frequently Asked Question
1. “Can Lyme disease cause tooth pain or sensitivity?”
People often ask if Lyme disease directly triggers toothaches, sensitivity to hot/cold, or unexplained dental pain. The answer ties to nerve inflammation and bacteria affecting oral tissues.
2. “What are the symptoms of Lyme disease in teeth?”
Searchers want a checklist of oral signs linked to Lyme, such as jaw pain, gum inflammation, loose teeth, or burning mouth syndrome.
3. “How does Lyme disease lead to dental problems like TMJ or gum disease?”
This FAQ explores the connection between Lyme bacteria, jaw joint dysfunction (TMJ), and gum issues caused by immune system strain.
4. “Can Lyme disease bacteria hide in teeth or root canals?”
Many worry that untreated Lyme bacteria infect dental work (e.g., root canals) or cavities, worsening systemic health. Studies confirm oral spirochetes are a risk.
5. “What holistic treatments help Lyme disease-related teeth issues?”
Patients seek natural options like ozone therapy, herbal rinses, or dietary changes to manage oral symptoms without harsh chemicals.
Conclusion
Lyme disease doesn’t just affect your joints or energy levels—it can silently harm your oral health, leading to issues like jaw pain, tooth sensitivity, and gum inflammation. If you’ve ever wondered, “Can Lyme disease really impact my teeth?” the answer is yes. The bacteria Borrelia burgdorferi, which causes Lyme disease, can trigger nerve inflammation, weaken the immune system, and even hide in oral tissues. This creates a perfect storm for dental problems, such as Lyme disease teeth sensitivity, TMJ disorders, or unexplained toothaches that don’t respond to typical treatments.
One of the biggest challenges is misdiagnosis. Symptoms like burning mouth syndrome or chronic dry mouth are often mistaken for routine dental issues, delaying proper Lyme treatment. Recent studies (2023) reveal that Lyme bacteria can linger in the mouth.